Description
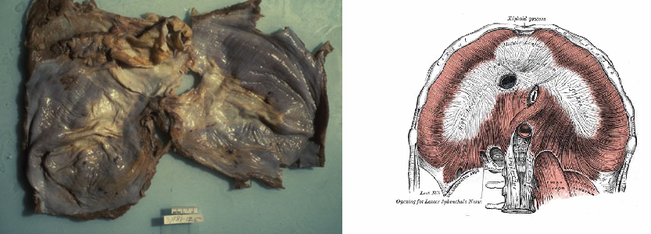
The thin layer of muscle that separates the chest cavity containing the lungs and heart from the abdominal cavity containing the intestines and digestive organs. It extends across the bottom of the rib cage.
Function
The diaphragm functions in breathing. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves in the inferior direction, thus enlarging the volume of the thoracic cavity (the external intercostal muscles also participate in this enlargement). This reduces intra-thoracic pressure: In other words, enlarging the cavity creates suction that draws air into the lungs.
Colour
White/Red.
Shape
Dome shaped.
Location
Base of the rib-cage.
Delimitation
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped musculofibrous septum that separates the thoracic from the abdominal cavity, its convex upper surface forming the floor of the former, and its concave under surface forming the roof of the latter. Its peripheral part consists of muscular fibers that take origin from the circumference of the inferior thoracic aperture and converge to be inserted into a central tendon.
The thin layer of muscle that separates the chest cavity containing the lungs and heart from the abdominal cavity containing the intestines and digestive organs. It extends across the bottom of the rib cage.
Function
The diaphragm functions in breathing. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves in the inferior direction, thus enlarging the volume of the thoracic cavity (the external intercostal muscles also participate in this enlargement). This reduces intra-thoracic pressure: In other words, enlarging the cavity creates suction that draws air into the lungs.
Colour
White/Red.
Shape
Dome shaped.
Location
Base of the rib-cage.
Delimitation
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped musculofibrous septum that separates the thoracic from the abdominal cavity, its convex upper surface forming the floor of the former, and its concave under surface forming the roof of the latter. Its peripheral part consists of muscular fibers that take origin from the circumference of the inferior thoracic aperture and converge to be inserted into a central tendon.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
